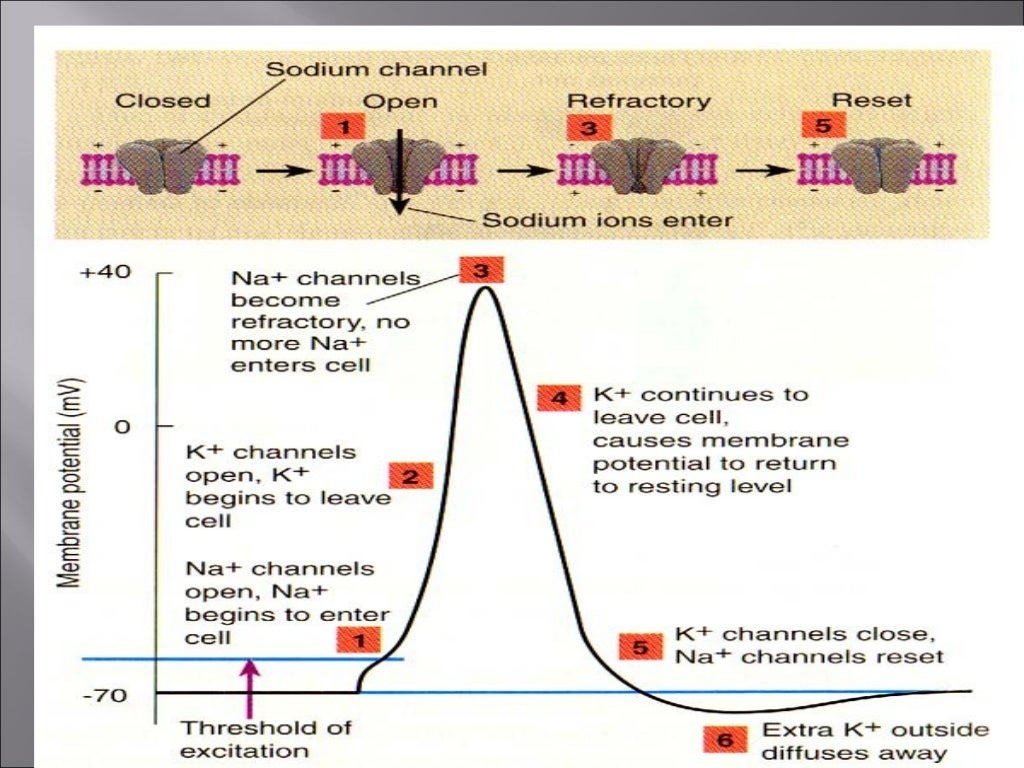
Membrane Potential Example . Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential.
from www.slideshare.net
Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Fred rieke and bertil hille. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential.
Resting membrane potential by DR. IRUM
Membrane Potential Example The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell.
From www.sciencefacts.net
Resting Membrane Potential Definition, Importance, and Diagram Membrane Potential Example Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known. Membrane Potential Example.
From med-sln.blogspot.com
Resting membrane potential (RMP) Medical Lecture Notes Membrane Potential Example The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Fred rieke and bertil hille. The membrane potential of the. Membrane Potential Example.
From studylib.net
Cell membrane potential Membrane Potential Example Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Numerous active. Membrane Potential Example.
From gen21kawa.github.io
Basic neuroscience 1 Cell membrane and membrane potential Genji Kawakita Membrane Potential Example The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Numerous active transports. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.youtube.com
Resting Membrane Potential YouTube Membrane Potential Example The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. The. Membrane Potential Example.
From education-portal.com
Membrane Potential Definition, Equation & Calculation Membrane Potential Example Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. The equilibrium potential of an ion is. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT GRADED POTENTIAL & ACTION POTENTIAL PowerPoint Presentation ID Membrane Potential Example Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Describe the physiological basis of the resting. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Resting Membrane Potential PowerPoint Presentation, free download Membrane Potential Example The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Fred rieke and bertil hille. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal.. Membrane Potential Example.
From eduinput.com
Resting Membrane Potential Membrane Potential Example Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: The equilibrium potential of. Membrane Potential Example.
From openbooks.lib.msu.edu
Membrane Potential Foundations of Neuroscience Membrane Potential Example Fred rieke and bertil hille. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.slideshare.net
Chapter3b Membrane Potential Example Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Fred rieke and bertil hille. Describe the elements of ionic. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Draw and label graph showing the changes in membrane potential Membrane Potential Example Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed in mmol/l) at the inner and. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.getbodysmart.com
Postsynaptic Neuron Resting Membrane Potential GetBodySmart Membrane Potential Example The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Describe the physiological basis of. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.biologyonline.com
Resting potential Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Membrane Potential Example Fred rieke and bertil hille. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.slideshare.net
Resting membrane potential by DR. IRUM Membrane Potential Example The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Ions, charge, potential gradients, forces, current, and. Numerous active transports embedded within the cellular membrane contribute to the creation of membrane potentials, as well as the universal. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of ions (expressed. Membrane Potential Example.
From eduinput.com
Resting Membrane Potential Membrane Potential Example The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Describe the elements of ionic electricity: Fred rieke and bertil hille. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. Describe the physiological basis of the resting. Numerous active transports embedded. Membrane Potential Example.
From drawittoknowit.com
Neurological System Resting Membrane Potential ditki medical Membrane Potential Example Describe the physiological basis of the resting. The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Numerous active transports. Membrane Potential Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Resting membrane potential and Action potentials PowerPoint Membrane Potential Example The membrane potential is measured using a reference electrode placed in the extracellular solution and a recording electrode placed in the cell soma. The equilibrium potential of an ion is defined as the point at which there is no net movement of the ion into or out of a cell. Resting membrane potential (em) originates from the different concentrations of. Membrane Potential Example.